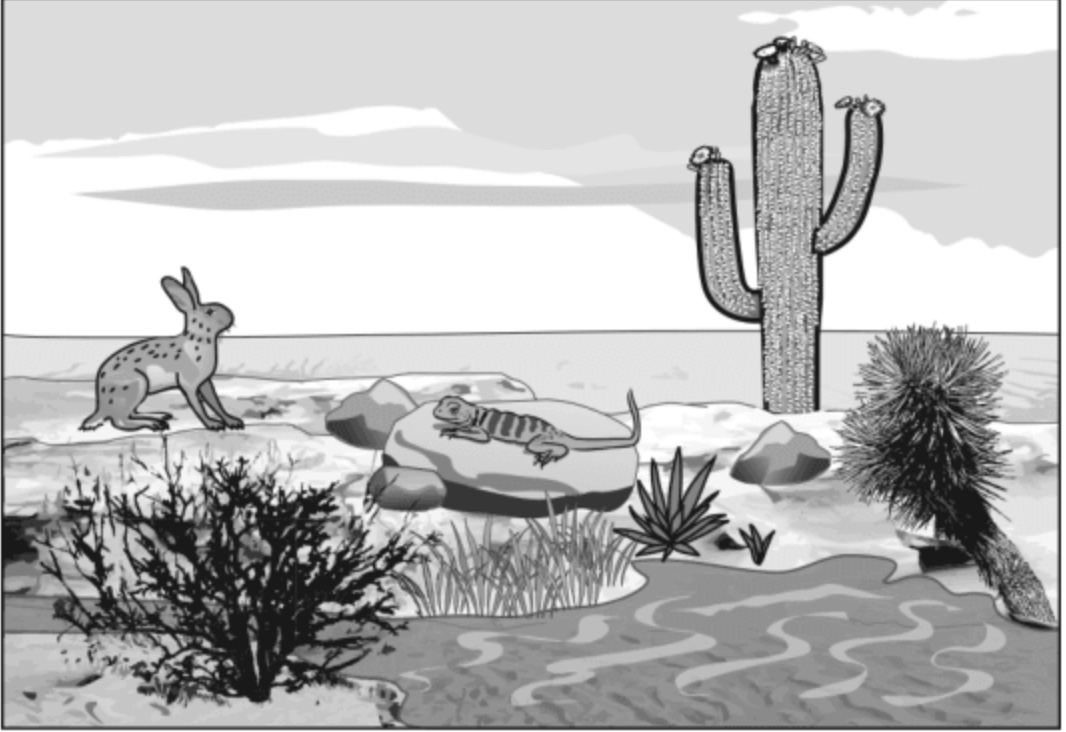
Unit 4 Pre-Test (2026)
star
star
star
star
star
Last updated 25 days ago
25 questions
8
S7L4.b
3
3
3
5
3
3
3
3
3
5
10
3
3
3
3
3
5
5
3
3
3
3
| Draggable item | arrow_right_alt | Corresponding Item |
|---|---|---|
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt |
| Draggable item | arrow_right_alt | Corresponding Item |
|---|---|---|
Parasitism | arrow_right_alt | Relationship where both organisms benefit |
Commensalism | arrow_right_alt | |
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt |
| Draggable item | arrow_right_alt | Corresponding Item |
|---|---|---|
Organism | arrow_right_alt | A single organism (a tiger) |
Population | arrow_right_alt | |
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt |
| Draggable item | arrow_right_alt | Corresponding Item |
|---|---|---|
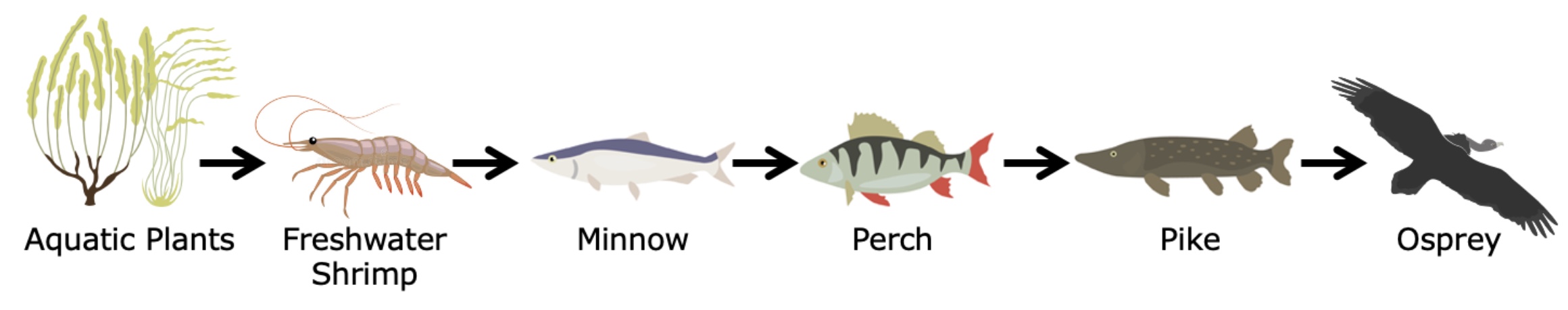
D - hawks | arrow_right_alt | producers |
A - grass | arrow_right_alt | primary consumers |
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt |