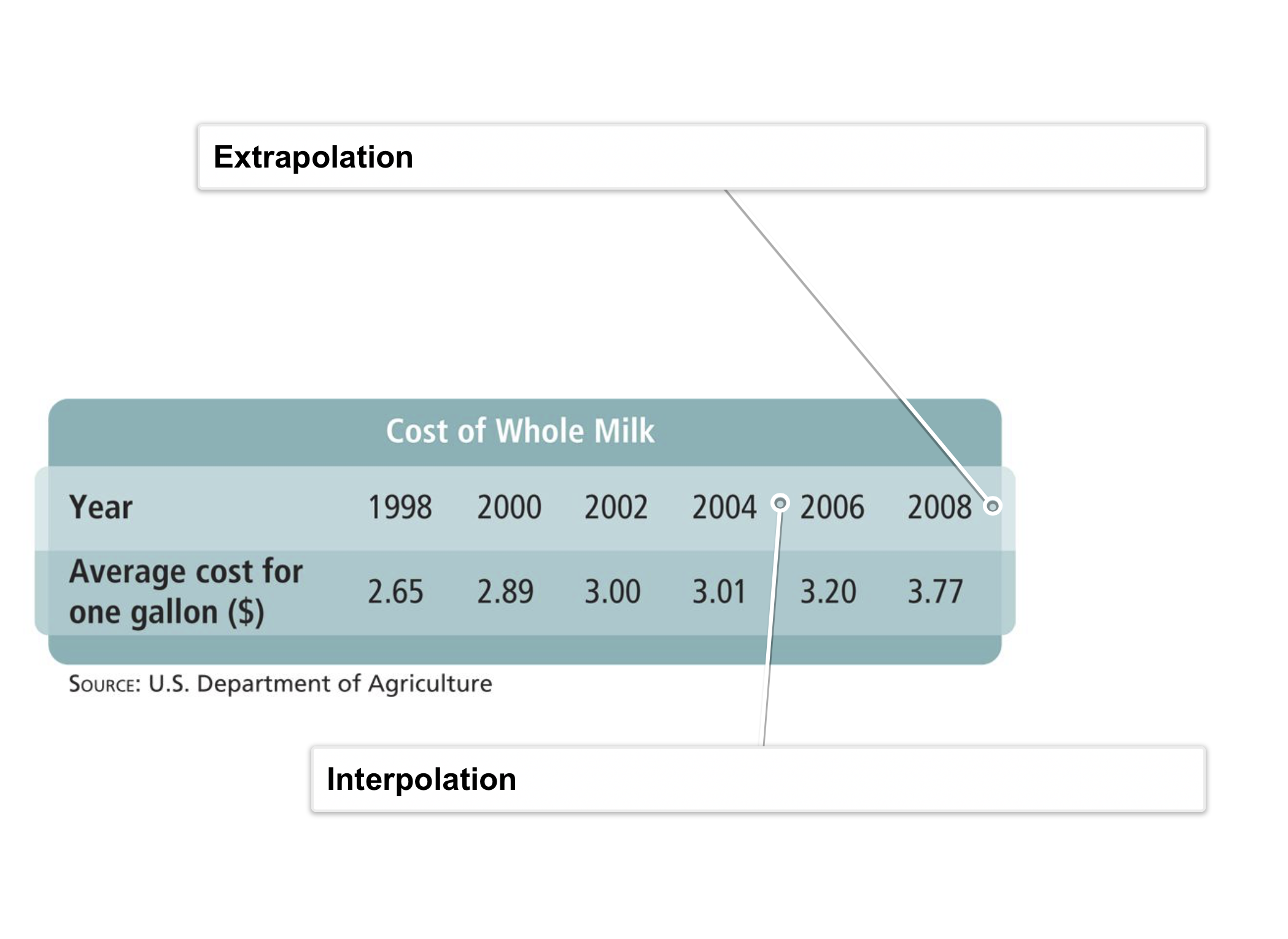
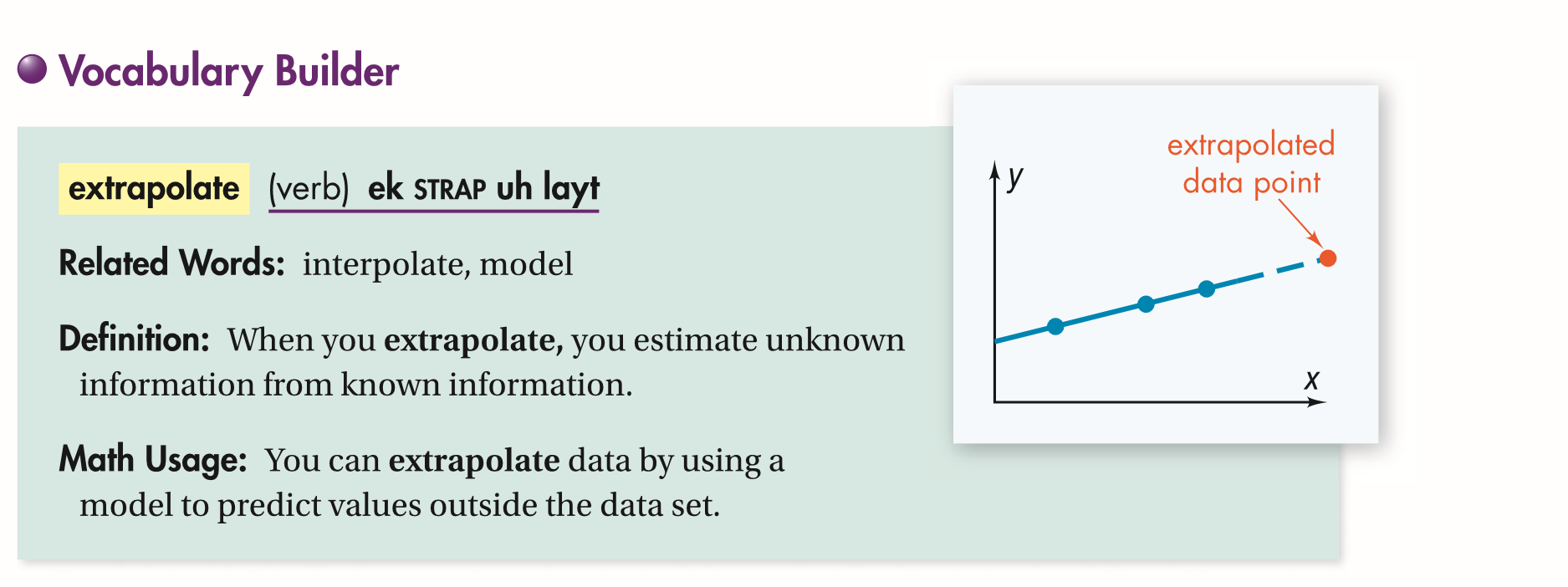
Algebra 2 5-8 Complete Lesson: Polynomial Models in the Real World
star
star
star
star
star
Last updated about 4 years ago
26 questions
Note from the author:
5
F.IF.5
10
F.IF.4
F.IF.5
30
F.IF.4
F.IF.5
F.IF.6
10
F.IF.5
F.IF.6
10
F.IF.5
10
F.IF.5
10
10
A.APR.5
10
A.APR.5
10
10
10
10
10
F.IF.7.a
10
10
100
10
F.IF.4
F.IF.5