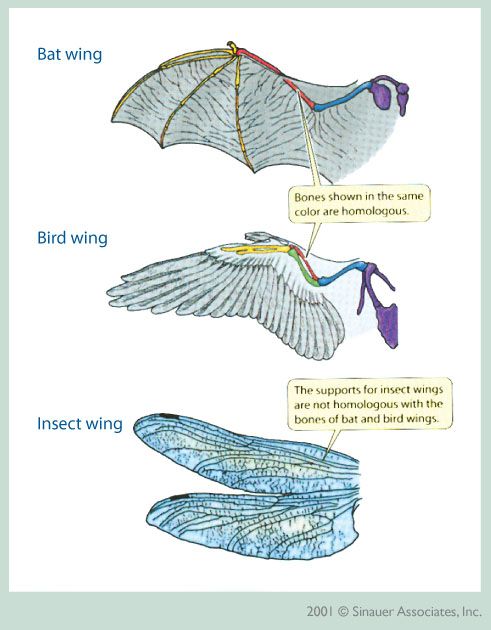
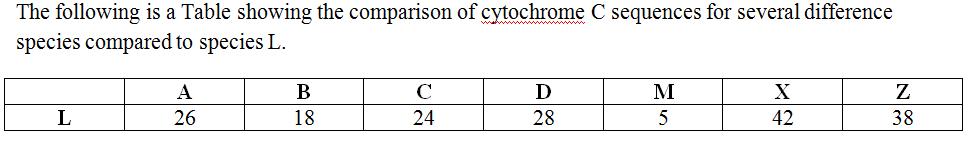
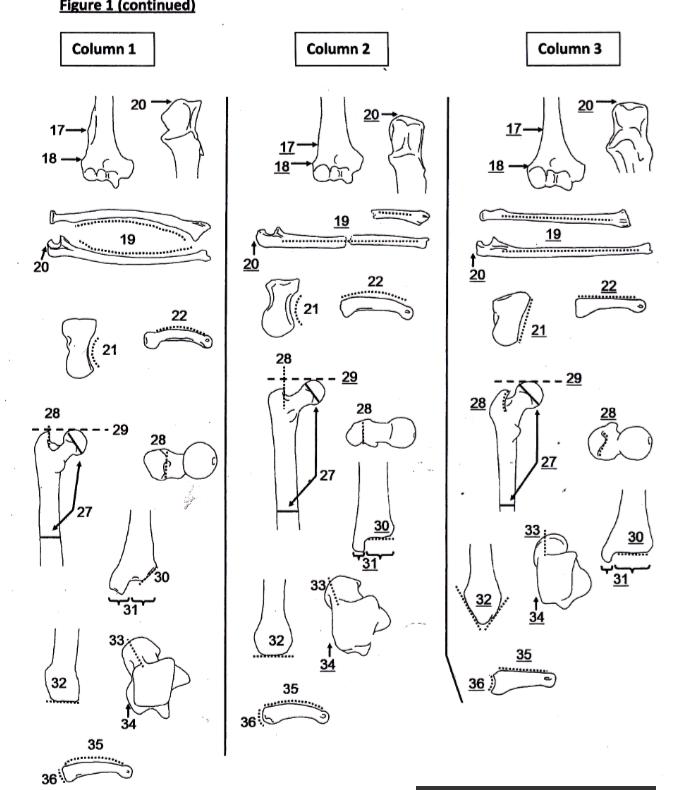
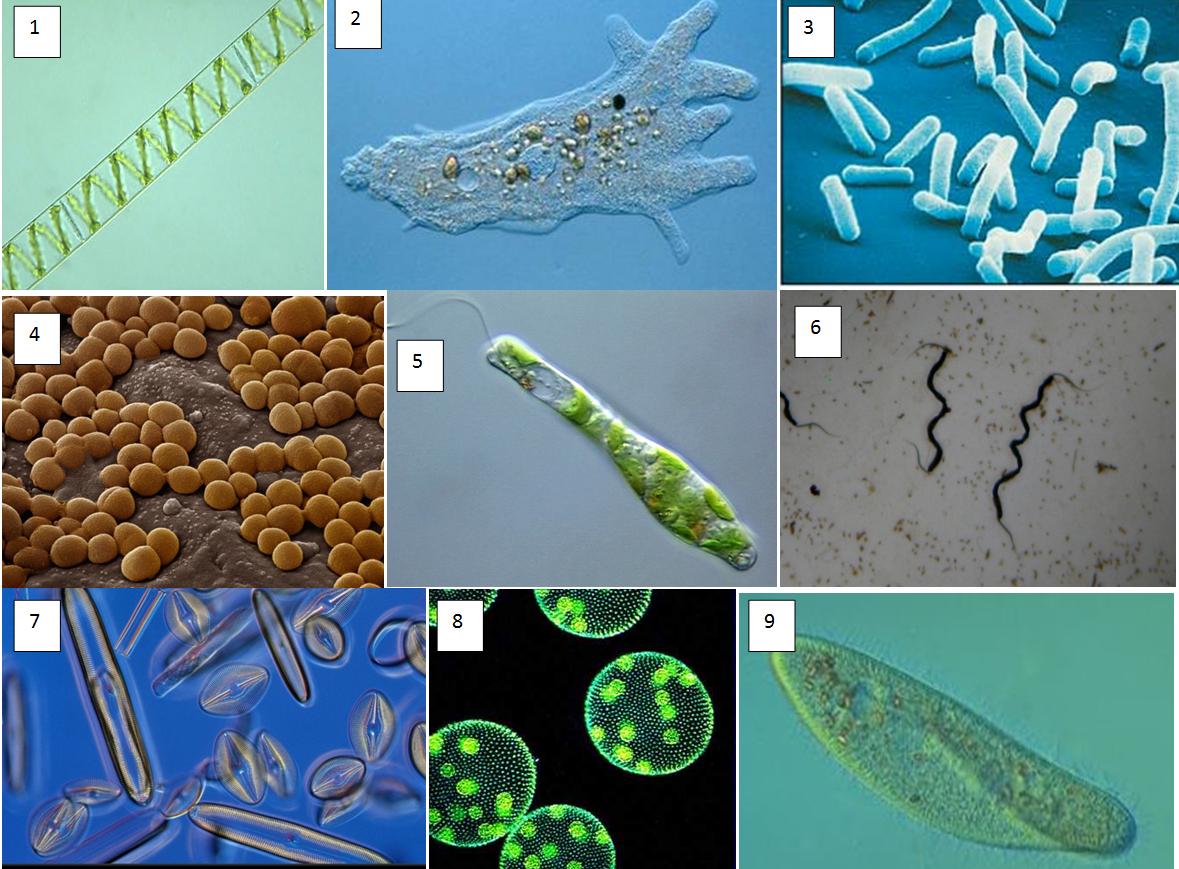
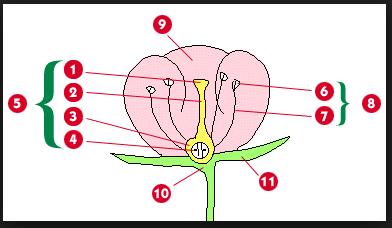
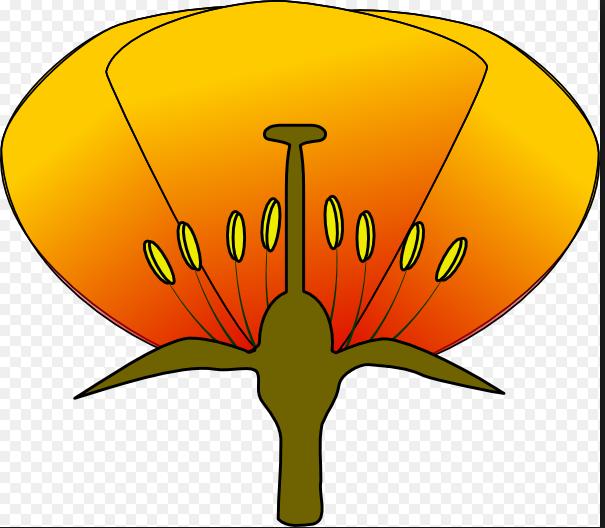
Lab Final Evolution through Plants (Labs 11, 12, 13, & 14)
star
star
star
star
star
Last updated almost 7 years ago
97 questions
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
3
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
12
6
3
5
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
2
1
2
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
2
2
2
1
2
1
1
1
2
1
1
1
1
2
1
2